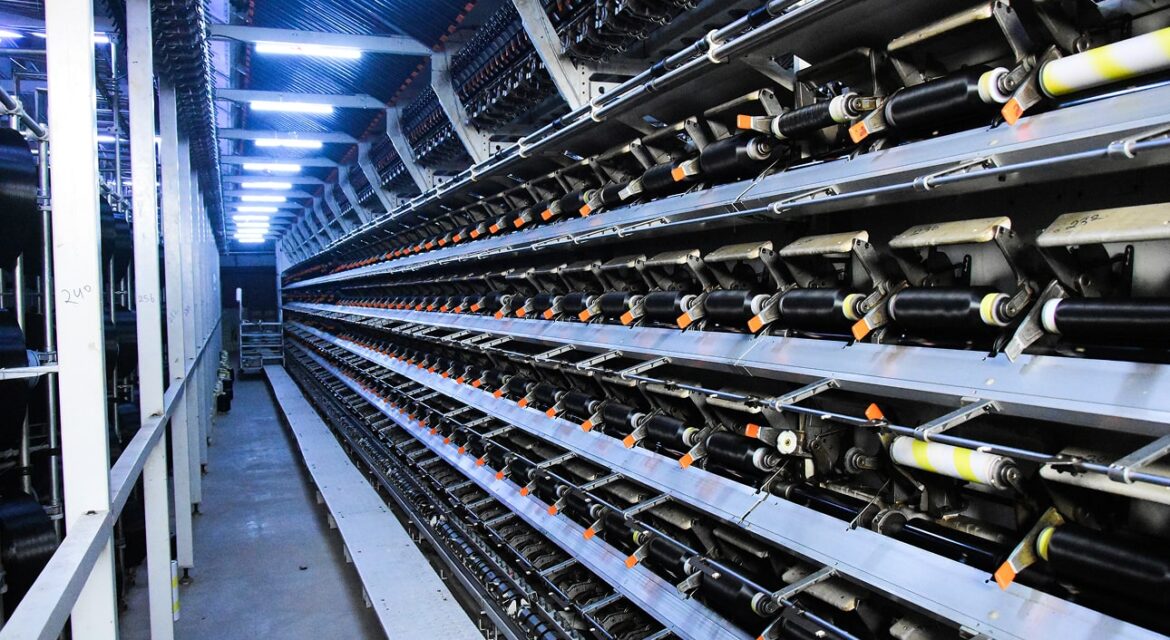
Yarn is an essential component in textile manufacturing. It is the primary material for fabric production and is crucial in creating textiles for clothing, home furnishings, and industrial applications. The ability to blend different fibres and enhance their properties has transformed modern textile production, making yarn indispensable in the industry.
This blog explores yarn’s significance, types, manufacturing processes, and applications, emphasising its essential role in global textiles.
Understanding Yarn and Its Importance
Textile manufacturing depends on materials that offer durability, flexibility, and adaptability to different applications. The quality of these materials determines the final product’s softness, strength, and resistance to wear.
Key Features of Textile Materials:
- Versatility – Used in apparel, home furnishings, and technical textiles.
- Durability – Designed for long-lasting wear and resistance to damage.
- Texture – Affects the feel, weight, and drape of the fabric.
- Dyeing Ability – Holds colours well, ensuring vibrant and lasting hues.
- Moisture Absorption – Some materials wick away sweat, making them ideal for activewear.
Innovations in material development have made it possible to enhance these properties, leading to better-performing textiles.
Types of Materials Used in the Textile Industry
Different materials are produced based on fibre composition, spinning method, and intended use.
1. Natural Fiber-Based Textiles:
Derived from organic sources, these materials are eco-friendly and breathable.
- Cotton-Based Fabric – Soft, durable, and widely used in clothing and home textiles.
- Wool-Based Fabric – Excellent for insulation, making it ideal for winter wear.
- Silk-Based Fabric – Luxurious and smooth, used in high-end fashion.
- Linen-Based Fabric – Lightweight and moisture-wicking, great for summer wear.
2. Synthetic Fiber-Based Textiles:
Engineered to enhance durability, flexibility, and moisture management.
- Polyester-Based Fabric – Wrinkle-resistant, widely used in sportswear.
- Nylon-Based Fabric – Stretchable and used in hosiery and performance wear.
- Acrylic-Based Fabric – Affordable, with wool-like properties, making it great for winter fabrics.
3. Blended Fiber-Based Textiles:
Combines different fibre types to improve functionality.
- Poly-Cotton Blend – Soft yet strong, ideal for everyday wear.
- Wool-Polyester Blend – Offers warmth and durability for outerwear.
- Viscose-Polyester Blend – Provides drape and breathability, which is common in premium garments.
Each material type serves a distinct purpose, allowing manufacturers to cater to diverse consumer needs.
Manufacturing Processes and Innovations
Advancements in textile production have led to improved techniques in material manufacturing, ensuring efficiency and sustainability.
1. Spinning Processes:
- Ring Spinning – Produces high-strength materials for delicate textiles.
- Open-End Spinning – A cost-effective method used for bulk production.
- Air-Jet Spinning – Creates smooth, uniform materials for high-end textiles.
2. Dyeing and Finishing Techniques:
- Solution-Dyed Fibers – Added colour during fibre formation for long-lasting vibrancy.
- Reactive Dyeing – Ensures better colour retention and fade resistance.
- Anti-Pilling Treatment – Enhances fabric longevity by reducing surface fuzz.
3. Smart Textile Technologies:
- Moisture-Wicking Fibers – Used in athletic apparel to keep fabrics dry.
- Anti-Microbial Fibers – Ideal for medical textiles, preventing bacterial growth.
- Specialty Fibers – Includes fire-resistant and water-repellent materials for industrial use.
Modern innovations continue to enhance textile quality, making fabric production more efficient and versatile.
Applications Across Various Industries
Textiles are fundamental components across multiple industries, contributing to various applications beyond fashion.
1. Apparel Industry:
- Casual Wear – Cotton-based fabrics dominate due to their comfort.
- Sportswear – Polyester and nylon materials offer flexibility and durability.
- Luxury Fashion – Silk and wool materials dominate high-end garments.
2. Home Textiles:
- Bedding & Linens – Soft textiles provide comfort and breathability.
- Curtains & Upholstery – Durable materials ensure longevity and fade resistance.
- Carpets & Rugs – Thick, high-strength fabrics enhance durability.
3. Industrial Applications:
- Automotive Textiles – Used in seat covers, airbags, and safety belts.
- Technical Textiles – Fire-resistant and high-strength materials for protective gear.
- Medical Textiles – Anti-bacterial and moisture-resistant textiles for hospitals.
The adaptability of textiles makes them an integral part of numerous industries worldwide.
Comparative Overview of Textile Types
| Material Type | Composition | Applications | Key Benefits |
| Cotton-Based | Natural Fiber | Apparel, Home Textiles | Soft, Breathable, Durable |
| Polyester-Based | Synthetic Fiber | Sportswear, Industrial Use | Strong, Wrinkle-Resistant |
| Wool-Based | Natural Fiber | Winter Wear, Blankets | Warm, Insulating |
| Silk-Based | Natural Fiber | Luxury Fashion, Accessories | Smooth, Lustrous |
| Acrylic-Based | Synthetic Fiber | Knitwear, Affordable Clothing | Wool-like Feel, Low Cost |
Source: Textile Industry Reports (2024)
This comparison highlights how different textile types cater to varied industrial and consumer needs.
Future Trends in Textile Production
1. Sustainable Innovations:
- Increased demand for organic cotton and recycled polyester materials.
- Bamboo textiles are gaining popularity as an eco-friendly option.
- Zero-waste production methods to minimise environmental impact.
2. Smart Textiles & Performance Materials:
- Phase-Change Fabrics – Adapt to temperature changes for enhanced comfort.
- Conductive Materials – Used in wearable technology and bright clothing.
- Odor-Resistant Fabrics – Ideal for sportswear and medical applications.
3. Customization & Digital Printing on Fabrics:
- Digital dyeing technologies allow intricate designs with minimal waste.
- Customised material production for niche markets like high-performance activewear.
As innovation progresses, textiles will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of industries worldwide.
Conclusion
Yarn remains one of the most significant elements in textile production. It supports industries such as fashion, home textiles, and technical applications. With continuous advancements in manufacturing techniques and material innovation, textiles continue to evolve, meeting the needs of modern consumers and businesses.
As the demand for high-quality textiles grows, the role of yarn in fabric production will remain vital. Whether used in casual clothing, luxury fabrics, or high-tech applications, yarn will continue to define the quality and functionality of textiles worldwide.