Introduction
Indian coal has been the backbone of the nation’s industrial and energy sectors for decades. As one of the world’s largest producers and consumers of coal, India relies heavily on this resource to fuel its growing economy. Coal in India plays an integral role in sectors such as power generation, steel production, and cement manufacturing, contributing significantly to the country’s GDP and industrial output. The Rawalwasia Group, a prominent name in the coal trade industry, has been instrumental in meeting the coal demands of these industries, ensuring the supply of high-quality Indian coal to power the nation’s growth.
India is experiencing an industrial revolution, and coal remains central to this transformation. As industries expand and urbanisation increases, coal’s importance in meeting energy demands and driving productivity has only intensified. In this article, we will explore the latest trends, needs, usages, and benefits of coal in India, focusing on how Indian coal is shaping the future of industrial growth.
The Importance of Indian Coal in Today’s Economy
Indian coal is an energy source vital to India’s industrial infrastructure. Coal-fired power plants generate about 70% of India’s electricity, making coal indispensable to the country’s energy security. Moreover, Indian coal is essential for industries central to the nation’s economic expansion, such as steel and cement manufacturing.
The demand for coal in India has been steadily rising, driven by a growing economy, urbanisation, and the government’s emphasis on infrastructure development. The Indian government has introduced reforms to boost domestic coal production and reduce import dependency. The goal is to achieve self-reliance in coal production, ensuring that Indian coal can meet the ever-increasing demands of the nation’s industries.
- Coal Production in India
Coal production in India has seen consistent growth over the past few years. India is the second-largest coal producer in the world, following China, with significant reserves located in states like Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and West Bengal. The government has implemented policies to enhance mining efficiency, encourage private sector participation, and ensure that coal production keeps pace with rising demand.
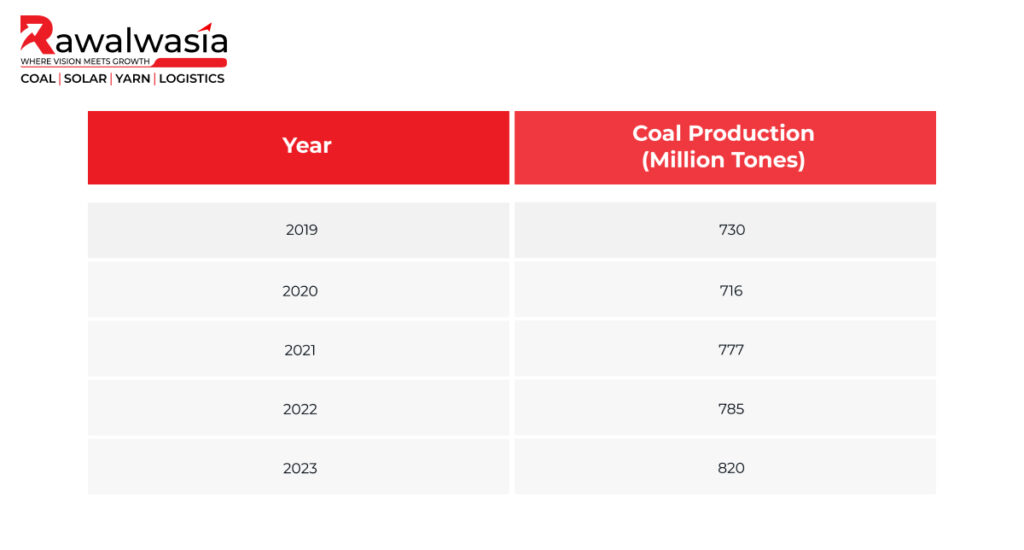
The table above shows a steady increase in coal production over the years, demonstrating India’s commitment to meeting domestic coal demand. However, coal imports are still required despite this growth, especially for high-quality coking coal used in steel manufacturing. The government has targeted reducing imports by increasing domestic coal production through better mining practices and technological advancements.
- Coal Imports and Exports
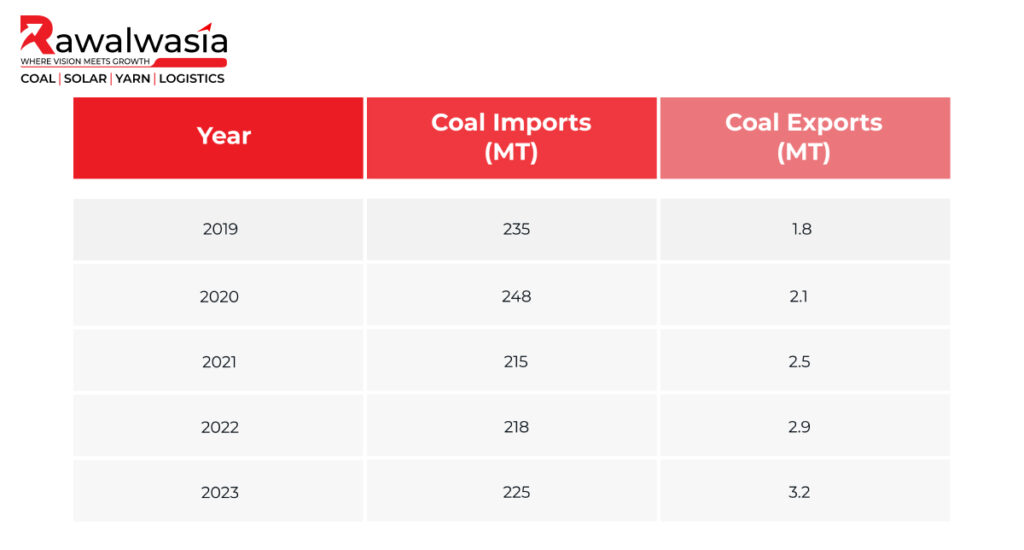
While India is a leading coal producer, it is also a significant importer, particularly of coking coal, which is essential for steel production. India imports coal from countries like Australia, Indonesia, and South Africa to meet the shortfall in domestic production. On the export front, Indian coal has a relatively limited presence in the global market. However, with rising production, India can potentially increase coal exports, particularly to neighbouring South Asian countries.
- Trends in Coal Demand in India
India’s demand for coal is growing in tandem with its economic and industrial expansion. The power sector remains the largest consumer of coal, accounting for nearly 70% of total consumption. However, other industries, such as steel, cement, and aluminium production, are also significant consumers of Indian coal.
One of the most notable trends in the Indian coal market is the increasing demand for coal in non-conventional sectors. Industries such as textiles, chemicals, and food processing have started using coal as a cost-effective energy source, increasing the demand for Indian coal.
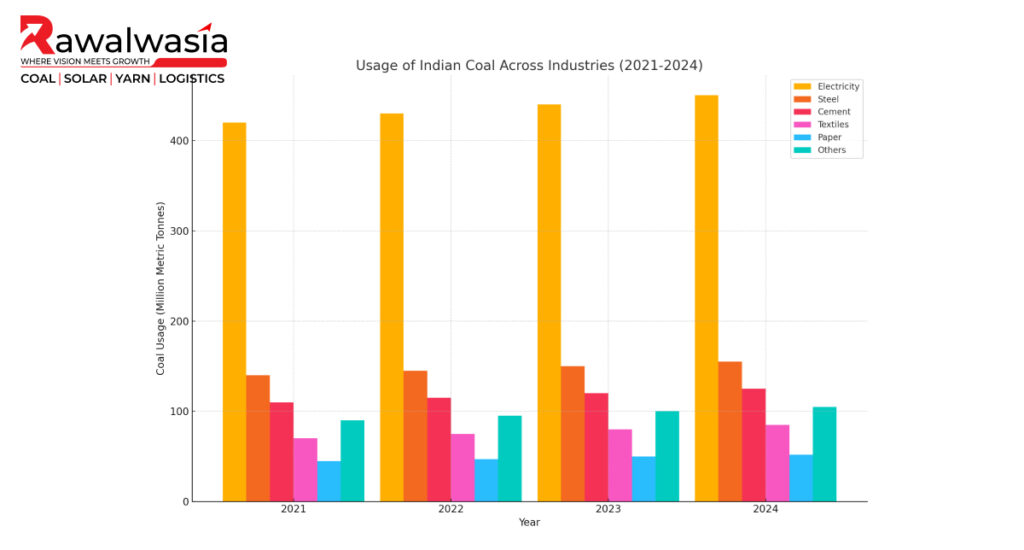
Usage of Indian Coal Across Industries
Indian coal is vital to a broad spectrum of industries, making it a key driver of the country’s industrial development. Here’s a breakdown of how different sectors use coal:
- Power Generation
Coal is India’s primary fuel for electricity generation, with thermal power plants accounting for around 70% of the nation’s power generation capacity. The availability and affordability of Indian coal make it the preferred choice for energy producers. As the nation’s energy demands continue to rise, coal’s role in powering India’s energy grid remains critical. The government has also prioritised improving the efficiency of coal-based power plants to ensure they can meet future energy needs.
- Steel Production
The steel industry is India’s second-largest consumer of coal, with coking coal being an essential component of steel manufacturing. Indian steel production is rising, driven by increasing demand from infrastructure projects, real estate, and manufacturing. Indian coal, while unsuitable for coking purposes, still plays a crucial role in providing energy to steel plants.
- Cement Industry
The cement industry is another significant consumer of Indian coal. As one of the fastest-growing sectors in the country, it relies heavily on coal for energy to produce clinker, the primary cement component. The demand for coal in the cement sector is expected to grow further, driven by the government’s push for infrastructure development and urbanisation.
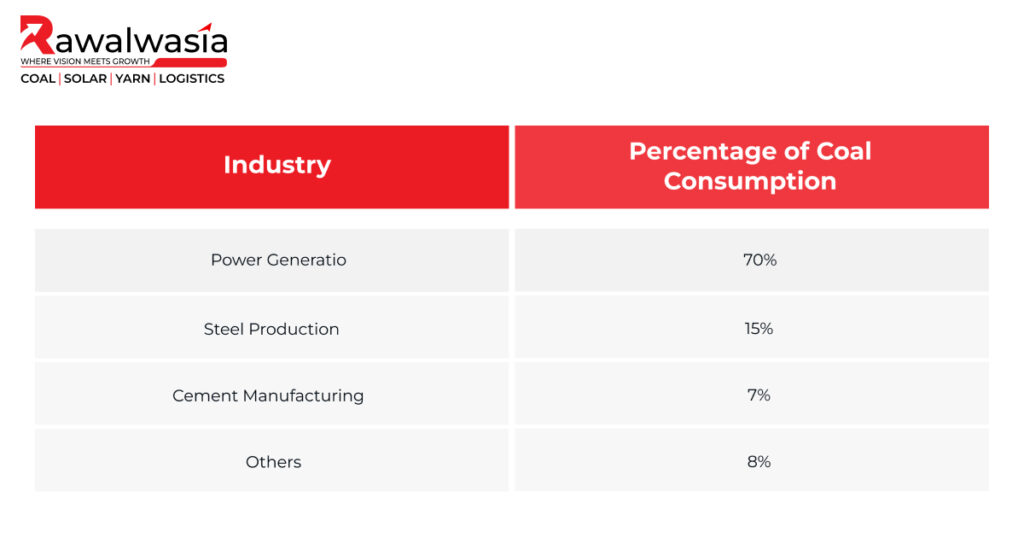
The table above highlights the distribution of coal consumption across different industries in India.
Benefits of Indian Coal for Businesses
Indian coal offers several advantages, making it a preferred choice for businesses across various sectors. Some of the key benefits include:
- Cost-Effective Energy Source
One of the most significant advantages of Indian coal is its cost-effectiveness. Coal is relatively cheap compared to alternative energy sources, making it an attractive option for industries looking to minimise operational costs. The affordability of Indian coal ensures that businesses can maintain their competitive edge in the market.
- Reliable Supply
India’s vast coal reserves ensure a consistent and reliable supply of coal to meet the needs of domestic industries. This reliability is essential for power generation and steel production, which require a steady coal flow to maintain operations. The government’s efforts to increase domestic coal production further enhance the reliability of coal as an energy source.
- Supporting Industrial Growth
Indian coal plays a pivotal role in supporting industrial growth. Steel, cement, and power generation industries rely heavily on coal to fuel their operations. As these industries expand, the demand for coal continues to rise, making coal an essential driver of India’s industrial progress.
Conclusion
Indian coal remains an indispensable resource for the country’s industrial and economic development. As the demand for coal in India continues to grow, companies like Rawalwasia Group are playing a crucial role in ensuring that businesses have access to high-quality coal to meet their energy and production needs. With significant coal reserves and a strong focus on increasing domestic production, India is well-positioned to maintain its status as one of the world’s leading coal producers.
Looking ahead, Indian coal will continue to be vital to the nation’s energy security and industrial growth. The Rawalwasia Group remains committed to supplying the highest-quality Indian coal to businesses across various sectors, ensuring they have the resources they need to thrive in an increasingly competitive market. As the coal industry evolves, companies can rely on Indian coal to power their future growth and success.






